When you start to ship freight at high volumes, it’s time to consider ocean freight. Here is your guide to everything ocean, from choosing the mode that’s right for you to calculating costs and transit times.
Ocean/Sea Freight Shipping Rates
How much will your shipment cost? You can use this free calculator to get instant ocean freight estimates.
Powered by the world’s largest digital freight network.

What are Freight Shipping Rates?
Freight shipping rates are the costs associated with transporting goods via various freight shipping methods, such as ocean, air, rail, or road. These rates can vary significantly depending on factors like the mode of transport, distance, volume, weight, and dimensions of the cargo, as well as market conditions and seasonal fluctuations.
When it comes to ocean freight rates, there are several key components that make up the total cost:
- Base freight rate: This is the basic cost of shipping your goods from the port of origin to the port of destination.
- Bunker Adjustment Factor (BAF): This is a surcharge that accounts for fluctuations in fuel prices.
- Currency Adjustment Factor (CAF): This surcharge compensates for exchange rate fluctuations.
- Terminal Handling Charges (THC): These are fees charged by the port authorities for handling containers at the origin and destination ports.
- Surcharges: Various additional fees may apply, such as for hazardous materials, peak season, or congestion at ports.
It’s essential to work with experienced freight forwarders who can help you navigate the complexities of freight shipping rates and find the most cost-effective solution for your specific needs. Platforms like Freightos.com enable you to compare rates from multiple providers instantly, making it easier to make informed decisions and optimize your shipping costs.
Freightos – The Digital Freight Shipping Platform: Costs, Prices, Rates, and More.
Instantly compare ocean freight shipping rates with freight quotes from vetted providers. Find the balance of price and transit time that works for your ocean freight.
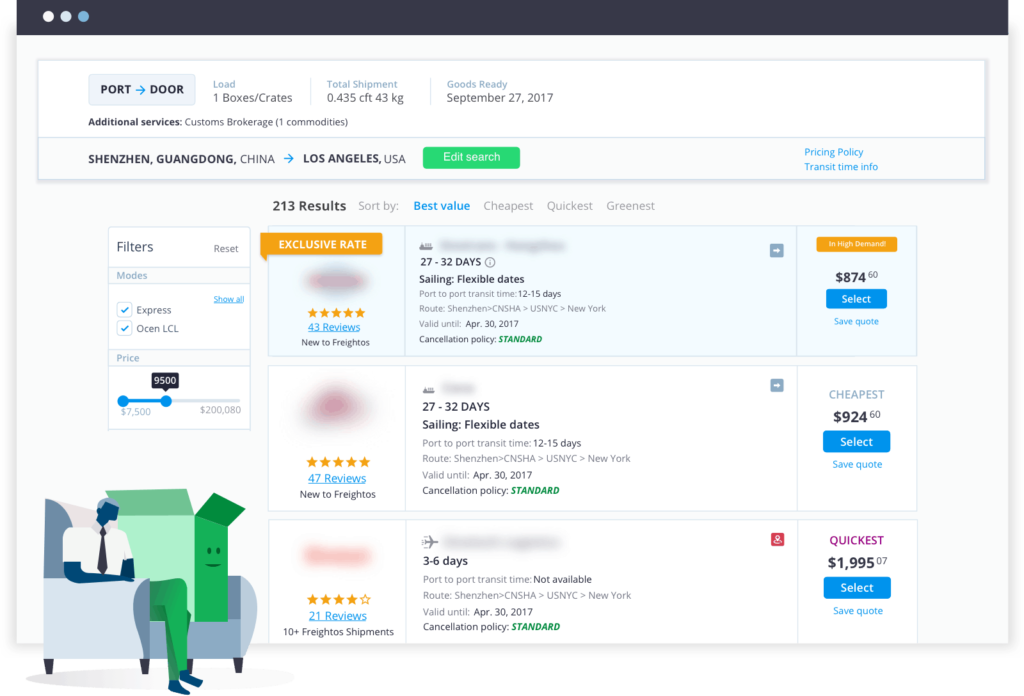
Our Ocean Freight Shipping Service
Freightos.com offers a comprehensive range of ocean freight shipping services, including instant quotes, freight forwarder comparison, online booking, customs clearance, cargo insurance, and shipment tracking.
As a global freight marketplace, we allow importers and exporters to choose from a variety of freight shipping options based on their specific needs. Freightos.com’s user-friendly interface and advanced technology also make it easy for small and large businesses to manage their freight shipments efficiently and cost-effectively. Discover how our reliable and seamless freight shipping service can simplify your logistics, providing the support you need for smooth operations.
LCL Shipping
Freightos offers a range of LCL (less-than-container load) shipping services to businesses looking to ship smaller quantities of cargo.
We provide instant quotes for LCL shipments, allowing businesses to compare rates from multiple forwarders and choose the best option based on their needs. Additionally, Freightos.com allows customs booking in-platform and easy communication with freight forwarders to help ensure that importers and exporters comply with all necessary regulations and requirements for LCL shipments.
FCL Shipping
For importers and exporters that need to transport larger quantities of cargo, Freightos.com offers a range of FCL (full container load) shipping services that include instant quotes for a variety of container types and sizes. Freightos.com can assist businesses with FCL shipping needs by providing instant quotes, a variety of container types and sizes, and support for customs clearance and documentation.
Ocean Freight Forwarders
Freightos.com works with many of the top and best ocean freight forwarders in the world.
The platform partners with leading freight forwarders to provide businesses with a wide range of shipping options, for both door-to-door and port-to-port shipments. Freightos.com’s advanced technology and online platform make it easy for businesses to compare rates and book freight shipments with its network of vetted forwarders. Our team of experts work closely with our forwarder partners to ensure that importers and exporters receive the highest quality of service throughout the shipping process.
What is Ocean Freight?
Ocean freight transport is the shipping of goods by sea via shipping containers.
Ocean freight is the most common mode of transport that importers and exporters use. In fact, a full 90% of goods are shipped by ocean freight and sea freight. The other international freight transport modes (courier, air freight, express) are all faster, but they are also more expensive. Smaller shipments, and products with a high value, generally go by these other modes.
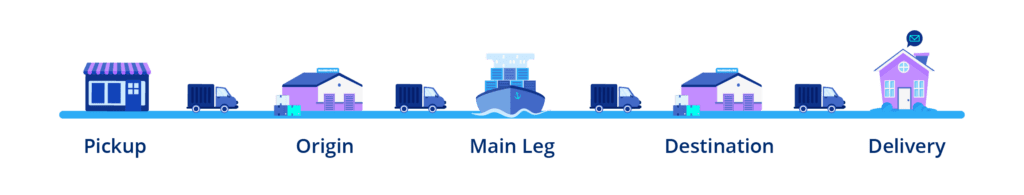
How Does Ocean Freight Work?
When you choose to ship your goods with ocean freight, your products will be packaged and possibly palletized either at the factory or by a third party. Your freight forwarder books space on a container vessel and your goods are shipped to the port to undergo a customs exam at the point of origin. Goods are then containerized into full containers or shared containers depending on whether you are shipping FCL or LC. Then the cargo is loaded onto ship for transportation.
Once the ship arrives at the destination port, goods pass through customs and once any duties and taxes are paid, are released. At this point, your goods will be shipped to a warehouse to be delivered to the final customer.
What Does Ocean Freight Mean?
Ocean freight means transporting goods through designated sea lanes by container vessel. This link in the supply chain is vital to cross-border trade that facilitates the movement of massive amounts of goods between countries.
There several shipping options available depending on the type of goods you are shipping. Full container load (FCL) shipping is when goods are containerized and shipped using standard sized 20 or 40 ft containers. For smaller quantities, LCL – or less than container load – means that shippers share container space since their volumes aren’t sufficient to fill a full container independently.
Ocean freight isn’t the only way to transport goods: for small, light, or high value products, many importers choose to ship by air. Air cargo is more expensive, but is faster and more secure. It’s also important to know that regulations for air cargo are more stringent than for ocean freight.
Freight Shipping by Sea
- Capacity and Value – One container can hold 10,000 beer bottles! And ocean freight is cheaper. As a rule of thumb, any shipment weighing more than 500 kg is too expensive for air freight. For light shipments, use this chargeable weight calculator to work out whether your freight shipment will be charged by actual weight or dimensional weight. For live international shipping rates see our FBX index.
- Fewer restrictions – International law, national law, carrier organization regulations, and individual carrier regulations all play their part in defining and restricting what goods are considered dangerous for transport. Generally, more products are restricted as air cargo than as ocean freight, including gases (e.g. lamp bulbs), all things flammable (e.g. perfume, Samsung Galaxy Note 7), toxic or corrosive items (e.g. batteries), magnetic substances (e.g. speakers), oxidizers and biochemical products (e.g. chemical medicines), and public health risks (e.g. untanned hides). For further information check out the Hazardous Material Table.
- Emissions – CO2 freight emissions from ocean freight is minuscule compared with air freight. For example, according to this research, 2 tonnes shipped for 5,000 kilometers by ocean freight will lead to 150 kg of CO2 emissions, compared to 6,605 kg of CO2 emissions by air freight shipping.

What are the downsides of Ocean Freight?
- Speed – Airplanes are about 30 times faster than ocean liners; passenger jets cruise at 575 mph, while slow-steaming ocean liners move at 16-18 mph. No surprise then, that a shipment going by air freight from China to the US usually takes at least 20 days more than by ocean freight.
- Reliability – Port congestion, customs delays, and bad weather conditions generally add much more days to ocean freight than air freight. To date, tracking technology in air freight is often more advanced than ocean freight. That means that ocean freight is more likely to get misplaced than air freight. This is especially true when the ocean shipment is less than a container load. That said, ocean freight is becoming more reliable thanks to digitization.
- Protection – Ocean freight is more likely to get damaged or destroyed than air cargo. That’s because it is in transit a lot longer, and because ships are more subject to movement. But don’t worry too much about ocean cargo falling off ships. The urban myth says 10,000 lost per year, but it’s more like 546 of the 120 million container movements per year that fall in the drink. Even less likely is piracy. Hotspots in recent years have included the Horn of Africa, the Gulf of Guinea, and the Malacca Straits.
Ocean Freight Services
Ocean and sea freight services break down to two further options: a full container load (FCL) and a less than container load (LCL). With LCL, several shipments are packed into one container. This means more work for the forwarder, there’s extra paperwork involved, as well as the physical work of consolidating various shipments into a container before the main transit and de-consolidating the shipments at the other end. This gives LCL three disadvantages:
- LCL takes more time to deliver than an FCL shipment. It’s typically recommended to allow an extra one or two weeks for LCL.
- There is an increased risk of damage, misplacement, and loss with LCL.
- LCL costs more per cubic meter.
Since shipping rates are lower for FCL, it may be worth using a full container once your freight shipment is large enough, even if your goods do not fill a full container. The tipping point for upgrading from LCL to FCL (the smallest sized container is a 20 footer) is somewhere around 15 cubic meters.
Sea Freight Rates Per KG
With the exception of particularly heavy goods, most LCL is priced per volume of goods, and not by weight.
For most products, use these rules of thumb for which selecting the most cost-effective mode:
- Freight shipments weighing more than 500 kg becomes uneconomic to go by air freight.
- Ocean freight is around $2-$4/kg, and a China-US shipment will take around 30-40 days or more.
- At about $5-8 per kilo, a China-US shipment between 150 kg and 500 kg can economically go air freight and will take around 8-10 days.
- Express air freight is a few days quicker, but more expensive.
- Packages that are lighter than 150 kg can economically go by courier (express freight).
Common Ocean and Sea Freight Costs, Rates, and Charges in Your Freight Quote:
Expect to see these items on ocean freight quotes and invoices:
- Customs security surcharges (AMS, ISF)
- Container Freight Station (these are the consolidation charges, and apply for LCL only)
- Terminal Handling charges (charges by the port authority)
- Customs brokerage
- Pickup and delivery
- Insurance
- Accessorial charges (fuel surcharges, handling hazardous materials, storage, etc)
- Routing charges (e.g. Panama Canal, Alameda Corridor)
Freight Shipping FAQs
FAQ
What is freight shipping?
Freight shipping is the transportation of goods in bulk by land, sea, or air. It involves the movement of large quantities of cargo, typically palletized or containerized, from one point to another using various modes of transport, such as trucks, trains, ships, or planes. Freight shipping is essential for businesses engaged in international trade and is a critical component of global supply chains.
What types of freight shipping are there?
Ocean Freight: This involves the transportation of goods by sea using container ships. It is the most common method for international freight shipping, especially for large volumes of cargo.
Air Freight: This mode uses planes to transport goods, offering faster transit times but at a higher cost compared to ocean freight. It is often used for time-sensitive, high-value, or perishable goods.
Road Freight: Goods are transported by trucks, which is a flexible and cost-effective option for domestic shipping and shorter distances.
Rail Freight: Trains are used to move large quantities of cargo over long distances, often as part of an intermodal shipping process in combination with other modes like ocean or road freight.
Intermodal Freight: This involves the use of multiple modes of transport, such as ships, trains, and trucks, to move goods from origin to destination, with the cargo remaining in the same container throughout the journey.
How does freight shipping work?
Freight shipping typically involves the following steps:
1. Planning: The shipper determines the type and quantity of goods to be transported, the origin and destination, and the desired timeline.
2. Booking: The shipper or their freight forwarder books space on the chosen mode of transport, such as a container ship or cargo plane.
3. Packing: The goods are prepared for shipping, which may involve palletizing, crating, or containerizing the cargo.
4. Inland Transportation: The goods are transported from the shipper’s location to the port, airport, or rail terminal.
5. Customs Clearance: Required documentation is submitted, and the goods are cleared for export by the relevant authorities.
6. Main Carriage: The cargo is transported by the chosen mode of transport to the destination country.
7. Customs Clearance: Upon arrival, the goods undergo import customs clearance, which may involve paying duties and taxes.
8. Inland Transportation: The cargo is transported from the port, airport, or rail terminal to the final destination.
9. Delivery: The goods are delivered to the consignee, completing the freight shipping process.
Throughout this process, various parties, such as freight forwarders, carriers, customs brokers, and port authorities, work together to ensure the smooth and efficient movement of goods across borders.
Do you need to know the seaport code for, say, the UK’s largest container port at Felixstowe? Check out this handy Seaport Code Finder. It’s GBFXT, by the way.